Book Value Vs Market Value Accounting

When the market value is less than book value the market.
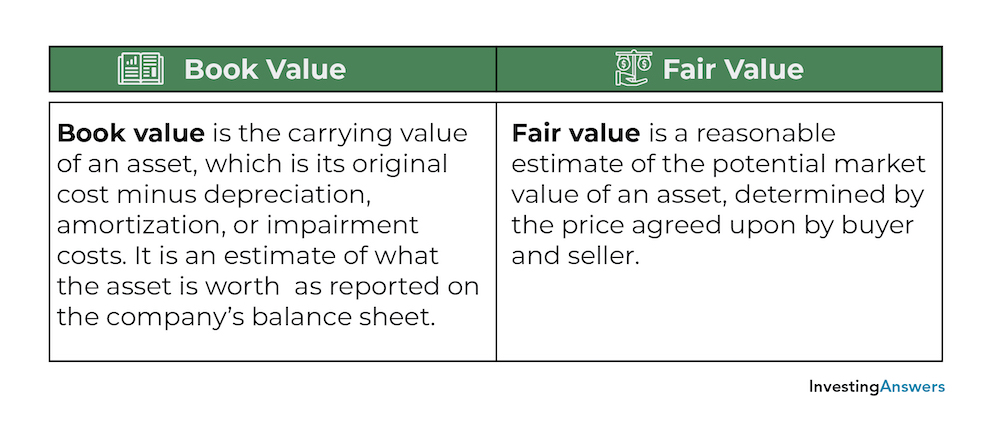
Book value vs market value accounting. Whereas market value is the price lower or higher than the book value which can be obtained in case of selling of that assets class or it is the price which is offered by a customer during the sale of the assets. Essentially the market value of an asset is a quantified reflection of the perception of the value of the asset by the market. Market value is higher than book value.
The book value of an asset is its original purchase cost adjusted for any subsequent changes such as for impairment or depreciation. Some assets might have a higher market value than book value meaning it would sell for more than what you paid for it minus depreciation. The amount of money you put into your company may outweigh its worth in the current market.
Its market value is higher than its book value resulting in a gain for your business. Book value is the actual worth of an asset of the company whereas market value is just a projected value of the firm s or asset s worth in the market. Market value is the price that could be obtained by selling an asset on a competitive open market.
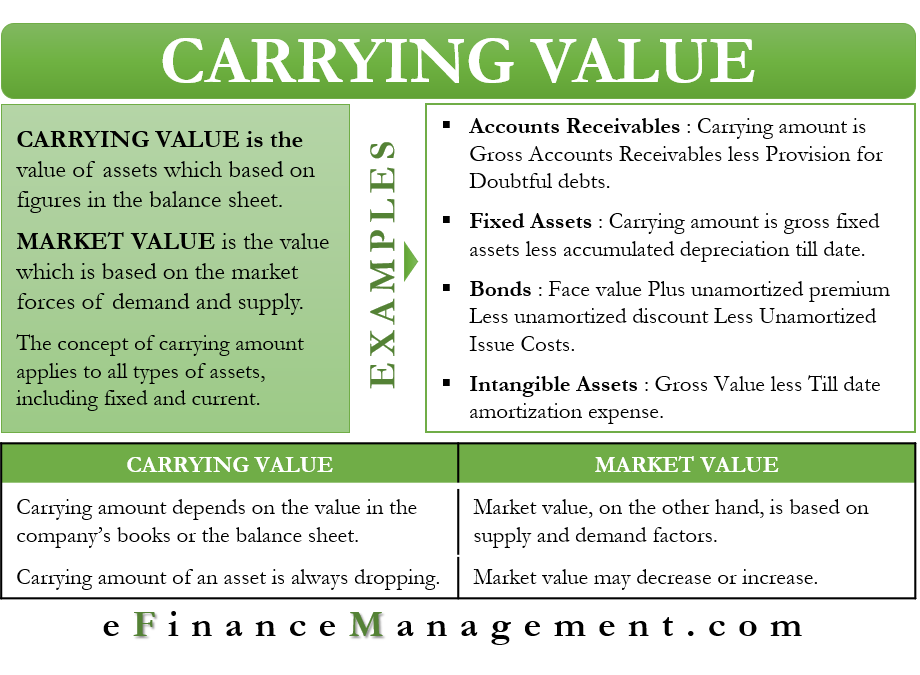
The book value is different from market value as it can be higher or lower depending on the asset in question and the accounting practices that affect book value such as depreciation amortization and impairment. Book value is equal to the value of the firm s equity. Book value is the recorded price of an asset which is shown in the balance sheet excluding depreciation.
For example a company has a p b of. The price to book p b ratio is a popular way to compare market value and book value. Book value simply implies the value of the company on its books often referred to as accounting value.
Book value gives us the actual worth of the assets owned by the company whereas market value is the projected value of the firms or the assets worth in the market. Market value is that current value of the firm or any asset in the market on which it can be sold. It is equal to the price per share divided by the book value per share.